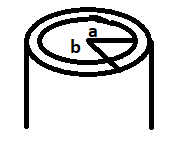
A long, cylindrical wire of radius b carries a current i distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point inside the wire at a distance a from the axis.
Given:
Radius of wire = b
Current distributed throughout the cross section = i
Diagram:
Formula used:
Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of the magnetic field for a closed surface is μ0 times the current enclosed by the surface.
![]() , where B = magnetic field, dl = line element, μ0 = magnetic permeability of vacuum, I = current enclosed.
, where B = magnetic field, dl = line element, μ0 = magnetic permeability of vacuum, I = current enclosed.
Since the current i is uniformly distributed throughout the cross section of the wire,
For an amperian loop of radius a(a<b) from the center of the wire,
I (current enclosed)
![]()
Where
i= total current distributed throughout the wire,
b = radius of the wire,
a = distance from the axis at which the magnetic field is to be found.
Hence, from Ampere’s circuital law,
![]()
since 2πa = circumference of Amperian loop of radius a, and I = enclosed current = ia2/b2.
Therefore, magnetic field at a distance a from the axis inside the wire, ![]()