Match the following equilibria with the corresponding condition.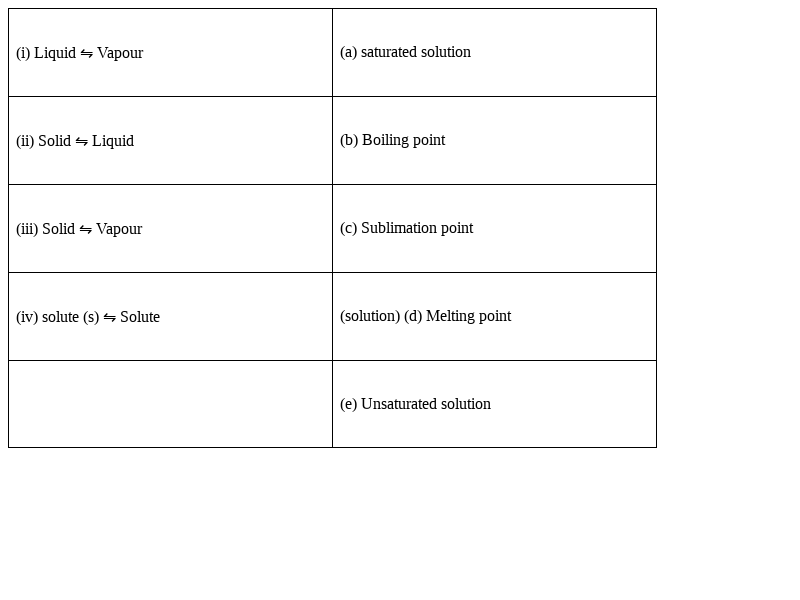
(i) Liquid ⇋ Vapour – (b) Boiling point
Explanation: when the vapour pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapour that temperature is called the boiling point of that substance. This keeps happening until an Equilibrium is attained i.e. the rate of evaporation=rate of condensation
(ii) Solid ⇋ liquid - (d) Melting point
Explanation: For any pure substance at atmospheric pressure, the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases are at Equilibrium is called the melting point of that substance. Here, the systems are in dynamic Equilibrium i.e. there is no change in product or reactant.
(iii) Solid ⇋ Vapour - (c) Sublimation point
Explanation: when a solid start converting into vapour phase without converting into a liquid that process is called the sublimation. This process happens at temperature and pressure below triple point (the point where all the phases co-exist in Equilibrium).
(iv) Solute (s) ⇋ Solute (solution) - (a) saturated solution
Explanation: A solution that contains the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved at a given temperature in the solvent is called a saturated solution. A dynamic Equilibrium exists between the solute molecules in solid-state and the solution.