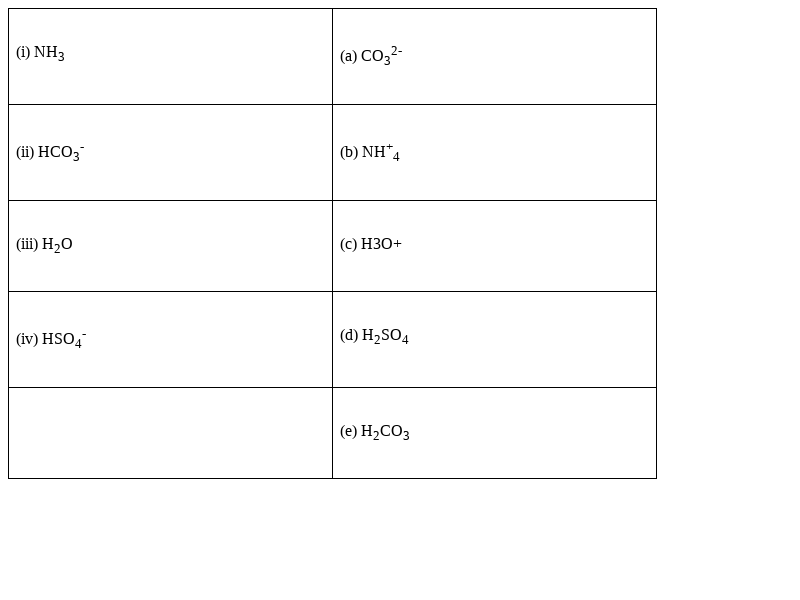
Match the following species with the corresponding conjugate acid
Species Conjugate acid
According to the bronsted-lowry theory, Conjugate acid-base pair is the species which differs by only one proton i.e. when you remove a proton from a parent acid it will become a conjugate base of that acid and that acid will be called a conjugate acid of that base.
(i) NH3 - (b) NH+4
![]()
The conjugate acid of a base is formed by the protonation (reception of an H+) of the acid. When an ammonium molecule accepts a proton (H+)), the ammonium cation (NH4+) is formed, as the nitrogen atom forms a coordinate bond with the hydrogen.
Explanation: The conjugate acid of ammonia is ammonium ion.
(ii) HCO3-- (e) H2CO3
![]()
Explanation: The bicarbonate ion(HCO3-) is a negatively charged base HCO3-, when we add a proton (H+)i.e. positively charged species on reacting with water we get the neutral conjugate acid, H2CO3.
(iii) H2O - (c) H3O+
![]()
Explanation: when water reacts with acid it acts as a base. When the proton (H+) will associate with water molecule it will form a hydronium ion (![]() ).
).
(iv) HSO4- - (d) H2SO4
![]()
Explanation: The conjugate acid of hydrogen sulphate ion is H2SO4.when hydrogen sulphate ion gains a proton i.e. H+ it gets converted into sulphuric acid (H2SO4).