A battery of emf 100 V and a resistor of resistance 10 kΩ are joined in series. This system is used as a source to supply current to an external resistance R. If R is not greater than 100 Ω, the current through it is constant up to two significant digits. Find its value. This is the basic principle of a constant-current source.
10mA
Given,
Emf of the battery, E= 100V
Resistance of series resistor, r= 10kΩ=10000kΩ
Resistance of external resistor, R=0-100Ω
Formula used:
A constant-current source is a power source that supply constant current to an external load, even if there is a change in load resistance.
When the battery is connected to the external resistance that vary from 0 to 100 Ω, the effective resistance will change across the potential difference provided by the battery.
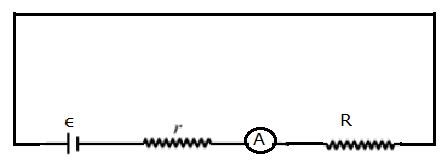
Solution:
Let’s find out the current when R=0Ω or when there is no external resistance is connected,
We know that, current i for a series resistor connection is
![]()
By substituting the known values, we get i as,
![]()
Now let’s take R as 2 Ω (or a low value like 1 Ω or so)
The value of current, i is
![]()
Where Rtot is the effective resistance across the battery. From the figure, Rtot can be calculated as,
![]()
Hence by putting R=2 Ω, we get i as,
![]()
Similarly, by putting R=100Ω , the highest possible, we get the current i as,
![]()
So, as the principle predicted, the value of the current, 1mA, does not change much, or it stays consistent till two significant digits.