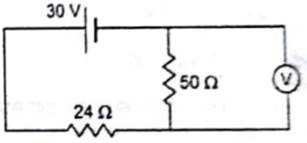
The voltmeter shown in figure reads 18 V across the 50 Ω resistor. Find the resistance of the voltmeter.
Concepts/Formula used:
Ohm’s Law:
Potential Difference (V) across a resistor of resistance R when current I passes through it is given by Ohm’s law:
![]()
Kirchhoff’s junction rule:
The sum of currents entering a junction is equal to the sum of currents leaving it.
Kirchhoff’s loop rule:
The sum of potential differences around a closed loop is zero.
Let us call the 24Ω resistance be R1 and 50Ω R2 . Let the resistance of voltmeter be RV .
It is given that the voltage across the voltmeter, V = 18V.
The given circuit can be drawn and labelled as follows:

Applying Kirchhoff’s loop rule,
![]()
![]()
Using Ohm’s law,
![]()
![]()
![]()
The potential difference across voltmeter and R2 is the same as they are in parallel.
Using Ohm’s law again,
![]()
![]()
Using Kirchhoff’s junction rule at X,
![]()
![]()
Finally, using Ohm’s law for the voltmeter, we get
![]()
![]()
Hence, the voltmeter has resistance 130Ω.