Match the following parameters with description for spontaneity: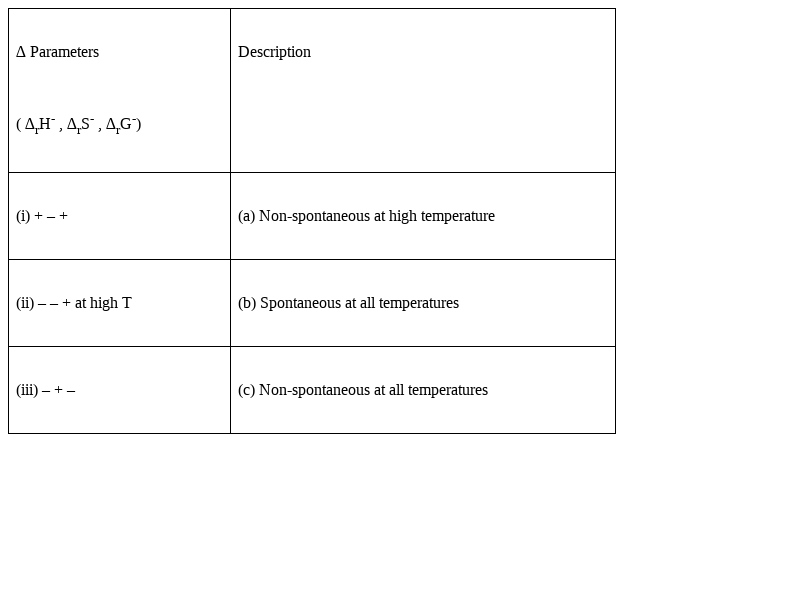
(i) + – + :(c) Reaction is Non spontaneous at all temperatures
(ii) – – + at high T :(a) Reaction is non-spontaneous at high
temperature
(iii) – + – :(b) Reaction is spontaneous at all temperature
Explanation: ∆rG- = ∆rH- - T∆rS-
∆G gives the criteria for spontaneity at constant temperature and pressure.
1. If ∆G is positive the process is non-spontaneous.
2. If ∆G is negative the process is spontaneous.
If a reaction has positive entropy and enthalpy change, the process can be spontaneous when T∆S is more enough to overweigh ∆H.
c. Entropy change in the system can be small in which Temperature must be large.
d. Entropy change in the system can be large in which temperature must be small
Because of the above reasons, reactions are often carried out at high temperature.
Reversible process in which the system is in perfect equilibrium with the surroundings. In chemical terms, reversible means, the reaction can proceed in any direction with a decrease in free energy, which is impossible. It is only possible when the energy of the system is minimum.
A+ B ![]() C + D
C + D
∆rG = 0
Gibbs free reaction in which all the reactant and product are in the standard state.
∆rG‑= -RT ln K
∆rG- = -2.303RT log K
Also,
∆rG- = ∆rH- - T∆rS- = -RT ln K
∆rH- is large and positive for strong endothermic reaction and the value of K is smaller than 1.
∆rH- is large and negative for exothermic reaction and the value of K is larger than 1. ∆rG- is also negative and large.
To get a large value of K we need a strongly exothermic reaction, hence we go for completion of the reaction.
∆rG- depend on ∆rS- and if entropy changes then the value of K also get affected, which depend on whether ∆rS- is positive or negative.