Two long wires carrying current I1 and I2 are arranged as shown in Fig. 4.1. The one carrying current I1 is along is the x-axis. The other carrying current I2 is along a line parallel to the y-axis given by x = 0 and z = d. Find the force exerted at O2 because of the wire along the x-axis.
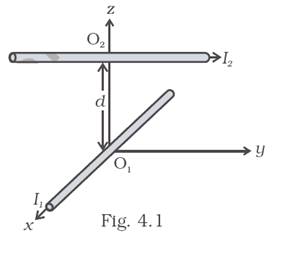
According, to the above given diagram wire with current I1 is in +ve x-axis and wire with current I �2 is in +ve y-axis. Now, according to Biot-savart law and right-hand thumb rule magnetic field due I1 current at O2 is given by ![]() where,
where,
μo is magnetic permeability in vacuum,
![]() is magnetic field vector,
is magnetic field vector,
I1 is current flowing in 1st wire,
and ![]() is the displacement vector for point we want to calculate the magnetic field.
is the displacement vector for point we want to calculate the magnetic field.
And will be in -ve y-axis direction, which means ![]() and
and ![]() for wire carrying I2 current will be parallel to each other. And force on current carrying straight wire due to uniform magnetic field is given by
for wire carrying I2 current will be parallel to each other. And force on current carrying straight wire due to uniform magnetic field is given by
F= I2![]() ×
× ![]() where,
where,
B is magnetic field strength;
I2 is current in the wire;
![]() is length vector of wire in direction of current.
is length vector of wire in direction of current.
So, since angle between ![]() and
and ![]() is 0o so, F is also 0.
is 0o so, F is also 0.
Hence, force on wire carrying current I2 due to magnetic field of wire carrying current I1 is zero (0).