There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Fig. 9.3). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by
Using Snell’s law,![]()
where n1 is the refractive index of medium 1, n2 is the refractive index of medium 2, i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction.
How do we measure r? We measure it from the normal in the direction in which the original ray would pass undeflected.
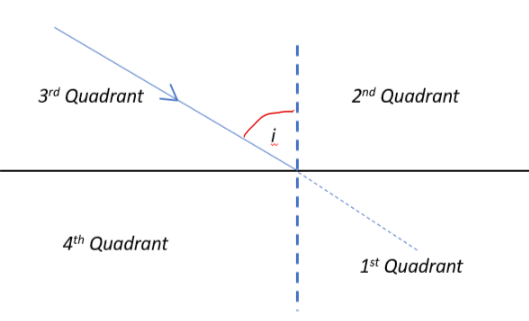
Note that i is always less than 90°. Hence, ![]() is always positive. Now, n2 is also positive but n1 is negative. Hence, sin(i) is also negative. Hence, r must be in the 3rd or 4th quadrant. The only time r is in the 3rd or 4th quadrant is in option (a).
is always positive. Now, n2 is also positive but n1 is negative. Hence, sin(i) is also negative. Hence, r must be in the 3rd or 4th quadrant. The only time r is in the 3rd or 4th quadrant is in option (a).
1