In an equilateral triangle ABC, if![]() , then
, then
Given in equilateral ΔABC, AD ⊥ BC.
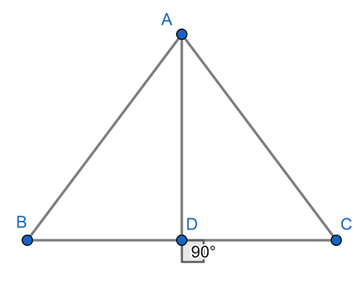
We know that the Pythagoras theorem state that in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In ΔABD,
⇒ AB2 = AD2 + BD2
⇒ AB2 = AD2 + ( 1/2BC)2 [∵ BD = 1/2BC]
⇒ AB2 = AD2 + ( 1/2AB)2 [∵ AB = BC]
⇒ AB2 = AD2 + 1/4AB2
∴ 3AB2 = 4AD2
1