A block of mass 2.0 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. (a) Show that the work done by the applied force does not exceed 40 J. (b) Find the work done by the force of gravity in that one second if the work done by the applied force is 40 J. (c) Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
:
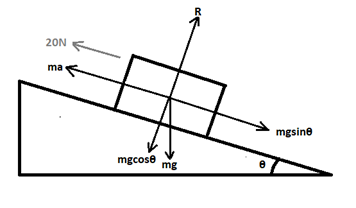
The mass of the block, m = 2 kg
Force that is being applied, F = 20 N
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
Time for which the force acts, t = 1 s
The applied force, F = mgsinθ + ma
20 = 2×10sin37° + 2×a
20 = 12 + 2a
⇒ a = 4 m/s2
The distance travelled by the block, s = 1/2 at2
= 0.5×4×1×1 = 2m
(a.) Maximum work done = Fs
= 20 × 2
= 40 J
(b.) If the work done by the applied force = 40 J
Distance travelled by the block = work done/ force applied
= 40/20 = 2m
Height corresponding to this distance, h = 2sin37° = 1.2 m
Work done by force of gravity = -mgh
= -2 × 10 × 1.2
= -24 J
(where the negative sign indicates the that displacement is against gravity)
(c.) Speed of the block after 1s = at = 4×1 = 4 m/s
Kinetic energy corresponding to this = 1/2 mv2
= 0.5 × 2 × 4 × 4
= 16 J