In a simultaneous throw of a pair of dice, find the probability of getting:
(i) 8 as the sum
(ii) a doublet
(iii) a doublet of prime numbers
(iv) a doublet of odd numbers
(v) a sum greater than 9
(vi) An even number on first
(vii) an even number on one and a multiple of 3 on the other
(viii) neither 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces
(ix) a sum less than 6
(x) a sum less than 7
(xi) a sum more than 7
(xii) at least once
(xiii) a number other than 5 on any dice.
Total number of outcomes when a pair of die is thrown simultaneously is:
Here the first number denotes the outcome of first die and second number the outcome of second die.
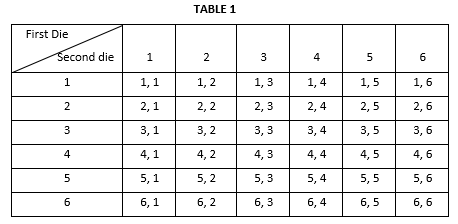
Total number of outcomes in the above table are 36
Numbers of outcomes having 8 as sum are: (6, 2), (5, 3), (4, 4), (3, 5) and (2, 6)
Therefore numbers of outcomes having 8 as sum are 5
Probability of getting numbers of outcomes having 8 as sum is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting numbers of outcomes having 8 as sum is ![]()
Total number of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes as doublet are: (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 4), (5, 5) and (6, 6)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes as doublet are 6
Probability of getting numbers of outcomes as doublet is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting numbers of outcomes as doublet is ![]()
(iii) a doublet of prime numbers
Total number of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes as doublet of prime numbers are: (1, 1), (3, 3), (5, 5)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes as doublet of prime numbers are 3
Probability of getting numbers of outcomes as doublet of prime numbers is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting numbers of outcomes as doublet of prime numbers is ![]()
Total number of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes as doublet of odd numbers are: (1, 1), (3, 3), (5, 5)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes as doublet of odd numbers are 3
Probability of getting numbers of outcomes as doublet of odd numbers is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting numbers of outcomes as doublet of odd numbers is ![]()
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having sum greater than 9 are: (4, 6), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having sum greater than 9 are 6
Probability of getting numbers of outcomes having sum greater than 9 is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting numbers of outcomes having sum greater than 9 is ![]()
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having an even number on first are: (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5) and (6, 6)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having an even number on first are 18
Probability of getting numbers of outcomes having An even number on first is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting numbers of outcomes having an even number on first is ![]()
(vii) an even number on one and a multiple of 3 on the other
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having an even number on one and a multiple of 3 on the other are: (2, 3), (2, 6), (4, 3), (4, 6), (6, 3) and (6, 6)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having an even number on one and a multiple of 3 on the other are 6
Probability of getting an even number on one and a multiple of 3 on the other is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting an even number on one and a multiple of 3 on the other is ![]()
(viii) neither 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces are: (3, 6), (4, 5), (5, 4), (5, 6), (6, 3) and (6, 5)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having neither 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces are 6
Probability of getting 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces is = ![]()
The probability of outcomes having 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces P(E) = ![]()
Probability of outcomes not having 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces is given by P(![]() ) =
) = ![]()
Therefore probability of outcomes not having 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces = P(![]() ) =
) = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting neither 9 nor 11 as the sum of the numbers on the faces is ![]()
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having a sum less than 6 are: (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having a sum less than 6 are 10
Probability of getting a sum less than 6 is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting sum less than 6 is ![]()
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having a sum less than 7 are: (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (4, 1), (4, 2), (5, 1)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having a sum less than 7 are 15
Probability of getting a sum less than 7 is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting sum less than 7 is ![]()
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having a sum more than 7 are: (2, 6), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having a sum more than 7 are 15
Probability of getting a sum more than 7 is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting sum more than 7 is ![]()
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Therefore Numbers of outcomes for atleast once are 11
Probability of getting outcomes for atleast once is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting outcomes for atleast once is ![]()
(xiii) a number other than 5 on any dice.
Total numbers of outcomes in the above table 1 are 36
Numbers of outcomes having 5 on any die are: (1, 5), (2, 5), (3, 5), (4, 5), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 5)
Therefore Numbers of outcomes having outcomes having 5 on any die are 15
Probability of getting 5 on any die is = ![]()
Therefore Probability of getting 5 on any die is ![]()
Probability of not getting 5 on any die P(![]() ) = 1 –P (E)
) = 1 –P (E)
P(![]() ) =
) = ![]()