In the adjoining figure, DE ‖ BC. Prove that
(i) ar(∆ACD) = ar(∆ABE),
(ii) ar(∆OCE) = ar(∆OBD).
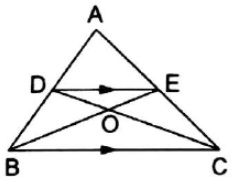
Given
AB ‖ DC
To prove that : (i) area(∆ACD) = area(∆ABE)
(ii) area(∆OCE) = area(∆OBD)
(i)
Here in the given figure Consider ![]() BDE and
BDE and ![]() ECD,
ECD,
we find that they have same base DE and lie between two parallel lines BC and DE
According to the theorem: triangles on the same base and between same parallel lines have equal
areas.
![]() Area of
Area of ![]() BDE = Area of
BDE = Area of ![]() ECD
ECD
Now,
Area of ![]() ACD = Area of
ACD = Area of ![]() ECD + Area of
ECD + Area of ![]() ADE ---1
ADE ---1
Area of ![]() ABE = Area of
ABE = Area of ![]() BDE + Area of
BDE + Area of ![]() ADE ---2
ADE ---2
![]() From 1 and 2
From 1 and 2
We can conclude that area(∆AOD) = area(∆BOC) (Since Area of ![]() ADE is common)
ADE is common)
Hence proved
(ii)
Here in the given figure Consider ![]() BCD and
BCD and ![]() BCE,
BCE,
we find that they have same base BC and lie between two parallel lines BC and DE
According to the theorem : triangles on the same base and between same parallel lines have equal
areas.
![]() Area of
Area of ![]() BCD = Area of
BCD = Area of ![]() BCE
BCE
Now,
Area of ![]() OBD = Area of
OBD = Area of ![]() BCD - Area of
BCD - Area of ![]() BOC ---1
BOC ---1
Area of ![]() OCE = Area of
OCE = Area of ![]() BCE - Area of
BCE - Area of ![]() BOC ---2
BOC ---2
![]() From 1 and 2
From 1 and 2
We can conclude that area(∆OCE) = area(∆OBD) (Since Area of ![]() BOC is common)
BOC is common)
Hence proved