In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral. A line through D, parallel to AC, meets BC produced in P.
Prove that ar(∆ABP) = (quad.ABCD).
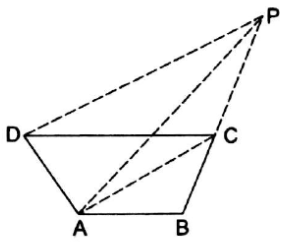
Given : ABCD is a quadrilateral in which a line through D drawn parallel to AC which meets BC produced in P.
To prove: area of (∆ABP) = area of (quad ABCD)
Proof:
Here, in the given figure
∆ACD and ∆ACP have same base and lie between same parallel line AC and DP.
According to the theorem : triangles on the same base and between same parallel lines have equal
areas.
![]() area of (∆ACD) = area of (∆ACP) -------------1
area of (∆ACD) = area of (∆ACP) -------------1
Now, add area of (∆ABC) on both side of (1)
![]() area of (∆ACD) + (∆ABC) = area of (∆ACP) + (∆ABC)
area of (∆ACD) + (∆ABC) = area of (∆ACP) + (∆ABC)
Area of (quad ABCD) = area of (∆ABP)
![]() area of (∆ABP) = Area of (quad ABCD)
area of (∆ABP) = Area of (quad ABCD)
Hence proved
13