In the adjoining figure, ∆ABC and ∆DBC are on the same base BC with A and D on opposite sides of BC such that ar(∆ABC) = ar(∆DBC).
Show that BC bisects AD.
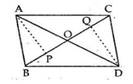
Given : ∆ABC and ∆DBC having same base BC and area(∆ABC) = area(∆DBC).
To prove: OA = OD
Construction : Draw AP ⊥ BC and DQ ⊥ BC
Proof :
Here area of ∆ABC = ![]() x BC x AP and area of ∆ABC =
x BC x AP and area of ∆ABC = ![]() x BC x DQ
x BC x DQ
since, area(∆ABC) = area(∆DBC)
![]()
![]() x BC x AP =
x BC x AP = ![]() x BC x DQ
x BC x DQ
![]() AP = DQ -------------- 1
AP = DQ -------------- 1
Now in ∆AOP and ∆QOD, we have
![]() APO =
APO = ![]() DQO = 90
DQO = 90![]() and
and
![]() AOP =
AOP = ![]() DOQ [Vertically opposite angles]
DOQ [Vertically opposite angles]
AP = DQ [from 1]
Thus by AAS congruency
∆AOP ![]() ∆QOD [AAS]
∆QOD [AAS]
Thus By corresponding parts of congruent triangles law [C.P.C.T]
![]() OA = OD [C.P.C.T]
OA = OD [C.P.C.T]
Hence BC bisects AD
Hence proved
14