In each of the figures given below, ![]() is a rectangle. Find the values of
is a rectangle. Find the values of ![]() and
and ![]() in each case.
in each case.
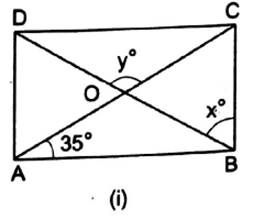
(i) Here, ABCD is rectangle.
We know that the diagonals of a rectangle are congruent and bisect each other.
∴ In ∆ AOB, we have OA = OB
This means that ∆ AOB is isosceles triangle.
We know that base angles of isosceles triangle are equal.
∴ ∠OAB = ∠OBA = 35°
∴ ∴ x = 90° − 35° = 55°
Also, ∠AOB = 180° − (35° + 35°) = 110°
∴ y = ∠AOB = 110° …Vertically opposite angles
Hence, x = 55° and y = 110°
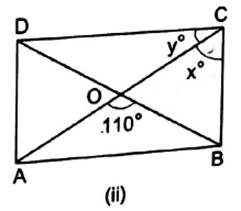
(ii) Here, ABCD is rectangle.
We know that the diagonals of a rectangle are congruent and bisect each other.
∴ In ∆ AOB, we have OA = OB
This means that ∆ AOB is isosceles triangle.
We know that base angles of isosceles triangle are equal.
∴ ∠OAB = ∠OBA = ![]() × (180° − 110°) = 35°
× (180° − 110°) = 35°
∴ y = ∠BAC = 35° … alternate angles with transversal AC
Also, x = 90° – y … ∵∠C = 90° = x + y
∴ x = 90° − 35° = 55°
Hence, x = 55° and y = 35°