A 5 m long ladder is placed leaning towards a vertical wall such that it reaches the wall at a point 4 m high. If the foot of the ladder is moved 1.6 m towards the wall, then find the distance by which the top of the ladder would slide upwards on the wall.
Let AC be the ladder of length 5 m.
BC = 4 m be the height of the wall, which ladder is placed.
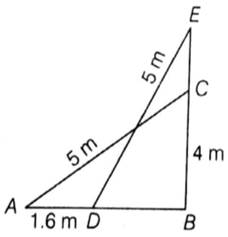
In right angled ∆EBD,
ED2 = EB2 + BD2 [by Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (5)2 = (EB)2 + (14)2 [ BD = 1.4]
⇒ 25 = (EB)2 + 1.96
⇒ (EB)2 = 25 –1.96 = 23.04
⇒ EB = √23.04 = 4.8
Now, EC = EB – BC = 4.8 – 4 = 0.8
Hence, the top of the ladder would slide upwards on the wall at distance 0.8 m.
6