PQ is a chord of length 4.8 cm of a circle of radius 3 cm. The tangents at P and Q intersect at a point T as shown in the figure. Find the length of TP.
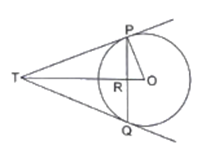
Given : A circle with center O and radius 3 cm and PQ is a chord of length 4.8 cm. The tangents at P and Q intersect at point T
To Find : Length of TP
Construction : Join OQ
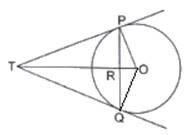
Now in △OPT and △OQT
OP = OQ [radii of same circle]
PT = PQ
[tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal]
OT = OT [Common]
△OPT ≅ △OQT [By Side - Side - Side Criterion]
∠POT = ∠OQT
[Corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent]
or ∠POR = ∠OQR
Now in △OPR and △OQR
OP = OQ [radii of same circle]
OR = OR [Common]
∠POR = ∠OQR [Proved Above]
△OPR ≅ △OQT [By Side - Angle - Side Criterion]
∠ORP = ∠ORQ
[Corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent]
Now,
∠ORP + ∠ORQ = 180° [Linear Pair]
∠ORP + ∠ORP = 180°
∠ORP = 90°
⇒ OR ⏊ PQ
⇒ RT ⏊ PQ
As OR ⏊ PQ and Perpendicular from center to a chord bisects the chord we have
![]()
∴ In right - angled △OPR,
By Pythagoras Theorem
[i.e. (hypotenuse)2 = (perpendicular)2 + (base)2]
(OP)2 = (OR)2 + (PR)2
(3)2 = (OR)2 + (2.4)2
9 = (OR)2 + 4.76
(OR)2= 3.24
OR = 1.8 cm
Now,
In right angled △TPR,
By Pythagoras Theorem
(PT)2 = (PR)2 + (TR)2 …[1]
Also, OP ⏊ OT
[Tangent at any point on the circle is perpendicular to the radius through point of contact]
In right angled △OPT, By Pythagoras Theorem
(PT)2 + (OP)2 = (OT)2
(PR)2 + (TR)2 + (OP)2= (TR + OR)2 …[From 1]
(2.4)2 + (TR)2 + (3)2 = (TR + 1.8)2
4.76 + (TR)2 + 9 = (TR)2 + 2(1.8)TR + (1.8)2
13.76 = 3.6TR + 3.24
3.6TR = 10.52
TR = 2.9 cm [Appx]
Using this in [1]
PT2 = (2.4)2 + (2.9)2
PT2 = 4.76 + 8.41
PT2 = 13.17
PT = 3.63 cm [Appx]