O is the center of a circle of radius 5 cm. At a distance of 13 cm from O, a point P is taken. From this point, two tangents PQ and PR are drawn to P the circle. Then, the area of quad. PQOR is
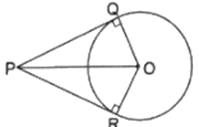
In Given Figure,
PQ = PR…[1]
[Tangents drawn from an external point are equal]
In △QOP and △ROP
PQ = PR [By 1]
OP = OP [Common]
OQ = OR [radii of same circle]
△QOP ≅△ROP
[By Side - Side - Side Criterion]
area(Δ QOP) = area(Δ ROP)
[Congruent triangles have equal areas]
area(PQOR) = area(Δ QOP) + area(Δ ROP)
area(PQOR) = area(Δ QOP) + area(Δ QOP) = 2[area(Δ QOP)]
Now,
OQ ⏊PQ
[Tangents drawn at a point on circle is perpendicular to the radius through point of contact]
So, QOP is a right - angled triangle at Q with OQ as base and PQ as height.
In △QOP,
By Pythagoras Theorem in △OPB
[i.e. (hypotenuse)2 = (perpendicular)2 + (base)2]
(OQ)2 + (PQ)2 = (OP)2
(5)2 + (PQ)2 = (13)2
25 + (PQ)2 = 169
(PQ)2 = 144
PQ = 12 cm
Area(ΔQOP) = 1/2 × Base × Height
= 1/2 × OQ × PQ
= 1/2 × 5 × 12
= 30 cm2
So,
Area(PQOR) = 2(30) = 60 cm2