Obtain the equivalent capacitance of the network in Fig. 2.35. For a 300 V supply, determine the charge and voltage across each capacitor.
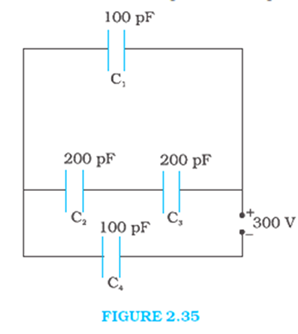
Capacitance of capacitor C1 = 100pF, C2 = 200pF, C3 = 200 pF, C4 = 100 pF.
Supply potential (V) = 300 V
Let the equivalent capacitance of capacitors C2 and C3(connected in series) be C'.
![]()
⇒ C’ = 100pF
Let the equivalent capacitance of capacitors C1 and C’(connected in parallel) be C’’.
![]() C’’ = C’ + C1 = 100 + 100 = 200pF
C’’ = C’ + C1 = 100 + 100 = 200pF
Let the equivalent capacitance of C’’ and C4 (connected in series) be C’’’.
![]()
⇒ C’’’ = 200/3pF
Thus, the equivalent capacitance of the circuit = 200/3 pF.
Now, Supply potential (V) = 300 V
Charge on C4 is given by,
Q4 = C’’’V = ![]() = 2 × 10-8C
= 2 × 10-8C
So, V4 = Q4/C4 = (2![]() 10-8)/(100
10-8)/(100![]() 10-12) = 200C
10-12) = 200C
Potential difference across C1 is given by, V1 = V-V4 = 300-200 = 100V
Charge on C1 is given by, Q1 = C1V1 = 100 × 10-12 × 100 = 10-8C
C2 and C3 having same capacitances have a potential difference of 100 V together.
Since C1 and C3 are in series, the potential difference across C2 and C3 is given by,V2 = V3 = 50V
Therefore charge on C2 is given by,Q2 = C2V2 = 200![]() 10-12
10-12![]() 50 = 10-8C
50 = 10-8C
And charge on C3 is given by,Q3 = C3V3 = 200![]() 10-12
10-12![]() 50 = 10-8C.
50 = 10-8C.
The charge and voltage across each capacitor are as follows:
Q1 = 10-8 C | V1 = 100V |
Q2 = 10-8 C | V2 = 50V |
Q3 = 10-8 C | V3 = 50V |
Q4 = 2 | V4 = 200V |