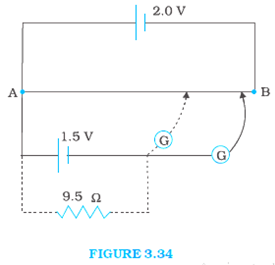
Figure 3.34 shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a 1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of 9.5Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
Resistance of the standard resistor, R = 10.0 Ω
Balance point for this resistance, l1 = 58.3 cm
Current in the potentiometer wire = i
Hence, potential drop across R, E1 = iR
Resistance of the unknown resistor = X
Balance point for this resistor, l2 = 68.5 cm
Hence, potential drop across X, E2 = iX
The relation connecting emf and balance point is,
E1/E2 = l1/l2
iR/iX = l1/l2
X = l1 × R/l2
X = 68.5 × 10/58.3
X = 11.749 Ω
Therefore, the value of the unknown resistance, X, is 11.75 Ω .
If we fail to find a balance point with the given cell of emf, E, then the potential drop across R and X must be reduced by putting a resistance in series with it. Only if the potential drop across R or X is lesser than the potential drop across the potentiometer wire AB, a balance point is obtained.