In a p-n junction diode, the current I can be expressed as
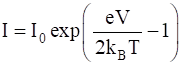
Where I0 is called the reverse saturation current, V is the voltage across the diode and is positive for forward bias and negative for reverse bias, and I is the current through the diode, kB is the Boltzmann constant (8.6 × 10–5 eV/K) and T is the absolute temperature. If for a given diode I0 = 5 × 10–12 A and T = 300 K, then
(a) What will be the forward current at a forward voltage of 0.6 V?
(b) What will be the increase in the current if the voltage across the diode is increased to 0.7 V?
(c) What is the dynamic resistance?
(d) What will be the current if reverse bias voltage changes from 1 V to 2 V?
Given,
Reverse saturation current (Io) = 5 × 10-12 A
Temperature (T) = 300K
The diode current (I) is given by the relation,
![]()
Where Io is the reverse saturation current
V is the voltage across the diode
kB is the Boltzmann’s constant
T is the absolute temperature
e is the electronic charge (1.6 × 10-19 C)
Note: The value of kB (in electron volts) is 8.6 × 10–5 eV/K and also 1.38 × 10-23 kg m2s-2K-1)
(a) For V = 0.6V,
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
So, I = 5.42 × 10-7 A
(b) For V = 0.7V,
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
So, I = 3.74 × 10-6 A
Hence, increase in current = 3.74 × 10-6 - 5.42 × 10-7 = 3.198 × 10-6 A
(c) ![]()
So, dynamic resistance = ![]()
i.e., Dynamic resistance = 31269.5 Ω = 31.26kΩ
(d) If the reverse bias voltage changes from 1V to 2V, then the diode current remains equal to reverse saturation current. So, dynamic resistance will be infinite.
NOTE: A diode is said to be in forward bias if the p-side and n-side are connected to the positive and negative terminals of the battery respectively. Electric current flowing through the diode in this condition is known as forward diode current. If the p-side is connected to the negative terminal and n-side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery, then the diode is said to be in reverse bias.