Two long and parallel straight wires A and B carrying currents of 8.0 A and 5.0 A in the same direction are separated by a distance of 4.0 cm. Estimate the force on a 10 cm section of wire A.
Given:
Current in wire A, IA = 8.0 A
Current in wire B, IB = 5.0 A
Distance between the conductors A and B, d = 4 cm
Length of conductor on which we have to calculate force, L = 10cm
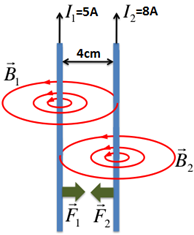
Intuitively we can break the problem into two parts,
1) the magnetic field due to wire A, at a distance d.
2) Then we introduce a current carrying conductor B, at distance d and find the force on it due to field created by wire A.
1) Field at distance d due to current IA in conductor A is given by,
![]() …(1)
…(1)
Where,
B = Magnetic field strength
I = current through the coil
�0 is the permeability of free space.
�0 = 4 × π × 10-7 TmA-1
d = distance of point P
By plugging the values in the equation (1), we get
![]()
⇒ |B| = 3.18 × 10-6T
2) Force on a current carrying conductor due to a magnetic field is given by
F = B × IB × L …(2)
Now by putting the values in equation (2) we get,
F = 3.18 × 10-6T × 5A × 0.1 m
⇒ F = 2 × 10-5N
So, the force on the 10 cm section on wire A is 2 × 10-5N. Since the current is flowing in the same direction the force will be attractive in nature.
Note: The force will be same on both the wires, we can use Newton’s third law of motion to such conclusion.