A chord 10 cm long is drawn in a circle whose radius is 5√2 cm. Find the areas of both the segments. [Take π = 3.14.]
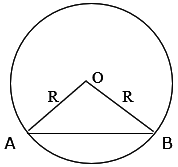
Consider the figure shown above.
In this, the triangle AOB is an isosceles triangle. So here we will construct a perpendicular bisector from O on AB and as this triangle is isosceles therefore this perpendicular will also act as median and angle bisector.
Therefore,

Draw a perpendicular bisector from O which meets AB at D and bisects AB, as ABO is an isosceles triangle therefore OD acts as a median.
So, consider right angle triangle AOD right angled at D
![]()
Let ∠AOD = θ ⇒ Perpendicular = AD and Hypotenuse = AO = R
Given Radius of circle = R = 5√2 cm
Length of chord AB = 10 cm, AD = 5 cm
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
⇒ θ = 45°
∴ ∠AOD = 45°
![]()
Area of minor segment = Area of sector – Area of right angle triangle
→ eqn1
![]()
Where R = radius of the circle and θ = central angle of the sector
![]()
![]()
![]()
∴ Area of sector = 39.25 cm2
Area of right angle triangle = 1/2 × base × height
As this is isosceles right-angle triangle
∴ height = base = 5√2 cm
Area of right angle triangle = 1/2 ×5√2×5√2 = ![]() = 25 cm2
= 25 cm2
Put the value of area of sector and area of right angle triangle in equation 1,
⇒ Area of minor segment = 39.25 -25
= 14.25 cm2
Area of major segment = πR2 – area of minor segment
![]()
![]()
⇒ Area of major segment = 157 – 14.25 = 142.75 cm2
Area of major segment is 142.75 cm2 and of minor segment is 14.25 cm 2.