In the given figure, ΔABC is right-angled at A. Semicircles are drawn on AB, AC and BC as diameters. It is given that AB = 3 cm and AC = 4 cm. Find the area of the shaded region.
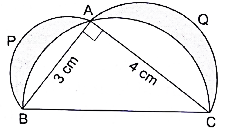
Here we will first find out the area of semicircle whose diameter is BC and then subtract the area of right angle triangle ABC from it and then we will subtract this result from the area of semicircles whose diameters are AB and AC.
Consider ∆ABC, ∠BAC = 90°
![]()
⇒ BC2 = 42 + 32
⇒ BC2 = 16 + 9
⇒ BC2 = 25
![]()
∴ BC = 5 cm
![]()
Area of semicircle whose diameter is AC
![]()
![]()
∴ Radius = 2 cm
![]()
∴ Area of semicircle = 2π cm2 –eqn2
Area of semicircle whose diameter is AB
![]()
![]()
∴ Radius = 1.5 cm
![]()
∴ Area of semicircle = 1.125π cm2→ eqn3
Area of semicircle whose diameter is BC
![]()
![]()
∴ Radius = 2.5 cm
![]()
∴ Area of semicircle = 3.125π cm2→ eqn4
![]()
![]()
⇒ Area of triangle PQR = 3×2
∴ Area of triangle PQR = 6 cm2→ eqn5
Now subtract equation 5 from equation 4,
⇒ Area of semicircle excluding ∆ABC = eqn4 – eqn5
⇒ Area of semicircle excluding ∆ABC = 3.125π – 6
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
∴ Area of semicircle excluding ∆ABC = 3.8214 cm2→ eqn6
Area of shaded region = eqn3 + eqn2 – eqn6
⇒ Area of shaded region = 2π + 1.125π – 3.8214
⇒ Area of shaded region = 3.125π – 3.8214
![]()
![]()
⇒ Area of shaded region = 9.8214 – 3.8214
∴ Area of shaded region = 6 cm2
Area of shaded region 6 cm2.