The angle of elevation of the top of a tower at a distance of 120 m from a point A on the ground is 45°. If the angle of elevation of the top of a flagstaff fixed at the top of the tower, at A is 60°, then find the height of the flagstaff. [Use √3 = 1.732.]
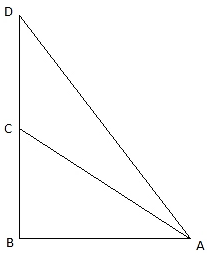
Let BC be the tower and CD be the flagstaff. Join C, A and D, A and A, B. We get two right-angled triangles ABC and BAD which are right-angled at B. By the problem, it is clear that ∠ BAC = 45° and ∠ BAD = 60°. We use trigonometric ratio tan for both the triangles using BC as height and AB as a base(for ∆ABC) and BD as height and AB as a base(for ∆ABD) to find the height of the flagstaff CD.
Let BC be x.
In ∆ABC we have,
![]()
or,
![]()
or,
x = 120
So, we get BC = 120m. In ∆ABD,
![]()
or,
![]()
or,
![]()
or,
![]()
So, height of the flagstaff = DC = 87.84m.