A ladder of length 6 metres makes an angle of 45° with the floor while leaning against one wall of a room. If the foot of the ladder is kept fixed on the floor and it is made to lean against the opposite wall of the room, it makes an angle of 60° with the floor. Find the distance between two walls of the room.
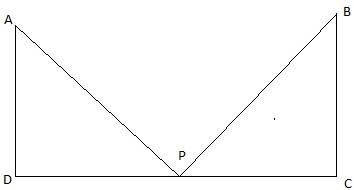
In the above figure, AD and BC are the two opposite walls of the same room. The ladder is fixed at the position say P on the floor. Join D,P and C. At first let it leans against the wall BC making an angle of 45° with the floor. Join B and P. We get a right-angled triangle BPC with right angle at C and ∠BPC = 45°. Again, when the ladder leans against the second wall AD, it makes an angle of 60° with the floor. Joining A and P, we get a right-angled triangle APD with right angle at D and ∠APD = 60°. We are to find the distance between the two walls, that is DC. Also given that, AP = PB = length of the ladder = 6 m.
To find DC, we separately find DP and PC from triangles APD and BPC respectively by using the trigonometric ratio cosine.
From ∆APD,
![]()
or,
![]()
Again, from ∆BPC,
![]()
or,
![]()
Hence, the distance between the two walls is, DC = DP + PC = 3 + 4.23 = 7.23m.