If the point P(x, y) is equidistant from the points A(5, 1) and B(– 1, 5), prove that 3x = 2y.
The point P(x, y) is equidistant from the points A(5, 1) and B(– 1, 5), means PA = PB
By distance formula, as shown below:
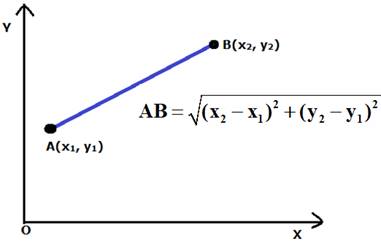
PA = √{(5 – x)2 + (1 – y)2}
= √{(25 + x2 – 10x) + (1 + y2 – 2y)}
⇒ PA = √{26 + x2 – 10x + y2 – 2y}
PB = √{(– 1 – x)2 + (5 – y)2}
= √{(1 + x2 + 2x + 25 + y2 – 10y)}
⇒ PB = √{(26 + x2 + 2x + y2 – 10y)}
Now, PA = PB
Squaring both sides, we get
26 + x2 – 10x + y2 – 2y = 26 + x2 + 2x + y2 – 10y
⇒ 12x = 8y
⇒3x = 2y
Hence proved.
11