Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than a α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
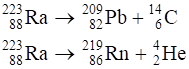
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
![]()
Where,
Δm = Mass defect (or) mass lost during reaction
c = speed of light
Take nuclear emission reaction given,
![]()
Energy (Heat) released during nuclear emission reaction,
We know that,
Mass of ![]() , m1 = 223.0185 u
, m1 = 223.0185 u
Mass of ![]() , m2 = 208.98107 u
, m2 = 208.98107 u
Mass of ![]() , m3 = 14.00324 u
, m3 = 14.00324 u
∴ ![]()
But, 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2
∴ ![]()
So, this reaction results in the emission of 31.848 MeV of energy.
Take nuclear emission reaction given,
![]()
Energy (Heat) released during nuclear emission reaction,
We know that,
Mass of ![]() , m1 = 223.0185 u
, m1 = 223.0185 u
Mass of ![]() , m2 = 219.00948 u
, m2 = 219.00948 u
Mass of ![]() , m3 = 4.00260 u
, m3 = 4.00260 u
∴ ![]()
But, 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2
∴ ![]()
So, this reaction results in the emission of 5.98 MeV of energy.
Since, both reactions are giving energy outside ( + ve), given reactions are energetically allowed.