Explain the principle and working of an electric motor with the help of a diagram. What is the function of a split ring commutator?
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle that – a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force.
Following are the essential parts of an electric motor.(i) Coil: It is a rectangular coil of insulated copper wire having large number of turns. (ii) A large permanent magnet provides strong magnetic field between its pole pieces. The coil rotates between these pole pieces. (iii) Split rings: The two ends of the coil are connected to two split rings, which are two halves of a slip rings. (iv) Brushes: Two carbon brushes keep in sliding contact with split rings.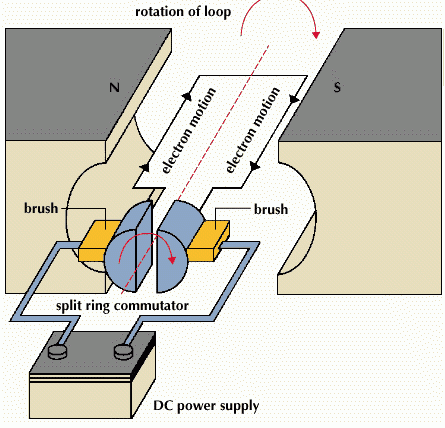 Working
Working
When a current is passed through the coil, the direction of current in AB and CD is in opposite direction but both are perpendicular to magnetic field. Therefore, by Fleming's left hand rule AB arm of the coil experiences an upward force and CD arm experiences a downward force. These two forces being equal and opposite to each other form a couple which rotates the coil. Arms BC and DA are parallel to the field and the force on them is zero. The forces, on AB and CD turn the coil in clockwise direction. After half revolution, the split rings change their position. Now S2 is in contact with brush B1 and S1 is in contact with B2. So the direction of current in the coil reverses. Therefore, AB now experiences downward force and CD upward force. The couple now acting on the coil again moves it in clockwise direction. Due to the function of split ring commutator and brushes, coil continues to turn in clockwise direction. Split ring commutator changes direction after every half rotation, so that the direction of current going in the coil also reverses and the arm of the coil which goes up in the first half, goes down in second half. As a result, the coil continues to rotate in one direction. Anything connected to the axis of the coil also rotates. So, the electrical energy given to the coil changes into mechanical energy.
Following are the essential parts of an electric motor.(i) Coil: It is a rectangular coil of insulated copper wire having large number of turns. (ii) A large permanent magnet provides strong magnetic field between its pole pieces. The coil rotates between these pole pieces. (iii) Split rings: The two ends of the coil are connected to two split rings, which are two halves of a slip rings. (iv) Brushes: Two carbon brushes keep in sliding contact with split rings.
 Working
WorkingWhen a current is passed through the coil, the direction of current in AB and CD is in opposite direction but both are perpendicular to magnetic field. Therefore, by Fleming's left hand rule AB arm of the coil experiences an upward force and CD arm experiences a downward force. These two forces being equal and opposite to each other form a couple which rotates the coil. Arms BC and DA are parallel to the field and the force on them is zero. The forces, on AB and CD turn the coil in clockwise direction. After half revolution, the split rings change their position. Now S2 is in contact with brush B1 and S1 is in contact with B2. So the direction of current in the coil reverses. Therefore, AB now experiences downward force and CD upward force. The couple now acting on the coil again moves it in clockwise direction. Due to the function of split ring commutator and brushes, coil continues to turn in clockwise direction. Split ring commutator changes direction after every half rotation, so that the direction of current going in the coil also reverses and the arm of the coil which goes up in the first half, goes down in second half. As a result, the coil continues to rotate in one direction. Anything connected to the axis of the coil also rotates. So, the electrical energy given to the coil changes into mechanical energy.
29