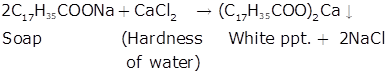Why do soaps not work in hard water?
The commonly used soaps are the sodium and potassium salts of higher fatty acids. They are soluble in water and give good lather to it. On the other hand, calcium and magnesium salts of higher fatty acids (calcium and magnesium soaps) are insoluble in water and do not produce lather. Hard water contains Ca2+and Mg2+ ions. When a sodium or potassium soap is added to hard water, it gets converted into an insoluble calcium or magnesium soap as shown ahead.
Due to the conversion of sodium or potassium soaps into calcium or magnesium soaps in the presence of hard water, the common soaps are unable to emulsify the greasy dirt and clean the dirty object. They do not produce lather with hard water. The calcium and magnesium soaps thus produced appear on the surface as insoluble sticky grey scum. This involves a waste of the common soap and the fabrics being washed get discoloured and hardened. This is why the commonly used sodium and potassium soaps can not be used as cleansing agents with hard water.