Explain the following with an example.
Kolbe’s reaction.
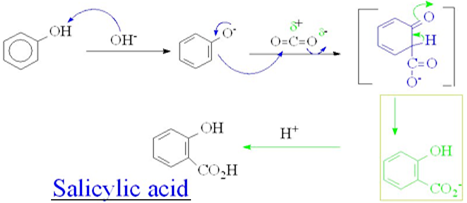
Kolbe’s Reaction: it is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by heating sodium phenoxide(the sodium salt of phenol)with carbon dioxide under pressure(100 atm,125°C), then treating the product with a sulphuric acid. The final product is salicylic acid (the precursor to aspirin).
The reaction is given as:

The mechanism is given below:
19