Explain the following with an example.
Williamson ether synthesis.
Williamson ether synthesis: It is an organic reaction forming ether from an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol (alkoxide). Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with primary alkyl halide via SN2 reaction.
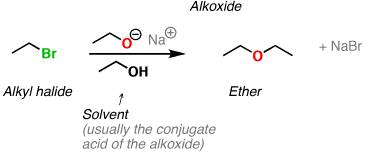
During this reaction, the main bonds broken is the C-Br bond and the new bonds formed are “C-O” bond.
21