Answer the following questions based on the P – T phase diagram of CO2:
(a) CO2 at 1 atm pressure and temperature – 60 °C is compressed isothermally.
Does it go through a liquid phase?
(b) What happens when CO2 at 4 atm pressure is cooled from room temperature at constant pressure?
(c) Describe qualitatively the changes in a given mass of solid CO2 at 10 atm pressure and temperature –65 °C as it is heated up to room temperature at constant pressure.
(d) CO2 is heated to a temperature 70°C and compressed isothermally. What changes in its properties do you expect to observe?
The P-T phase diagram of CO2 is as follows:
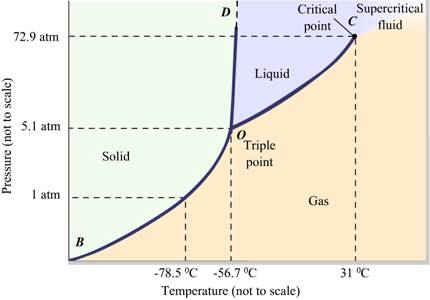
(a) Since the temperature -60° C lies to the left of 56.7° C on the curve i.e., it lies in the region vapour and solid phase, carbon dioxide will condense directly into the solid without becoming liquid.
(b) Since the pressure 4 atm is less than 5.1 atm the carbon dioxide will condense directly into solid without becoming liquid.
(c) When a solid CO2 at 10 atm pressure and -65° C temprature is heated, it is first converted into liquid. A further increase in temperature brings it into the vapour phase. At P = 10 atm, if a horizontal line is drawn parallel to the Temperature-axis, then the points of intersection of this line with the fusion and vaporization curve will give the fusion and boiling points of CO2 at 10 atm.
(d) Since 70° C is higher than the critical temperature of CO2, the CO2 gas cannot be converted into liquid state on being compressed isothermally at 70° C. It will remain in the vapour state. However, the gas will deviate from its perfect gas behaviour with increasing pressure.