Calculate a) ![]() and b) the equilibrium constant for the formation of NO2 from
and b) the equilibrium constant for the formation of NO2 from
NO and O2 at 298K
NO (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) ⇌ NO2 (g)
Where
![]() (NO2) = 52.0 kJ/mol
(NO2) = 52.0 kJ/mol
![]() (NO) = 87.0 kJ/mol
(NO) = 87.0 kJ/mol
![]() (O2) = 0 kJ/mol
(O2) = 0 kJ/mol
For the given reaction,
NO (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) ⇌ NO2 (g)
Given:
Standard free energy change of the formation of the product (NO2)
⇒ΔfG° (NO2) = 52.0 kJ/mol
Standard free energy change of the formation of one reactant (NO)
⇒ΔfG° (NO) = 87.0 kJ/mol
Standard free energy change of the formation of second reactant(O2)
⇒ΔfG° (O2) = 0 kJ/mol
a) Calculation of ΔG°
ΔG° = Difference in free energy of the reaction when all the reactants and products are in the standard state (1 atmospheric pressure and 298K) Hence,
ΔG° = ∑ ΔfG° (Products) - ∑ ΔfG° (Reactants)
⇒ΔG° = ΔfG° (NO2) – [ΔfG° (NO) + 1/2 ΔfG° (O2)]
⇒ΔG° = 52.0 – [87.0 + 1/2 x 0]
⇒ΔG° = -35.0 kJ mol-1
b) Equilibrium constant for the formation of NO2 from NO and O2 at 298K
From standard free change of a reaction, we know that,
ΔG° = -2.303 RT log Kc
Where, ΔG° is the standard free change of a reaction, value of ΔG° is -35000 (calculated in part(a))
R = gas constant, value of R is 8.314 J/mol-K
T= Absolute temperature, value of T is 298K (given)
Kc= Equilibrium constant
Using the formula, we write,
log Kc = 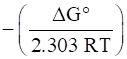
⇒log Kc = 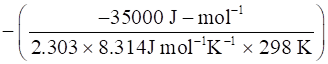
⇒log Kc = 6.134
∴ Kc = antilog (6.134)
⇒Kc = 1.361 x 106