Calculate the pH of the resultant mixtures:
A. 10 mL of 0.2M Ca(OH)2 + 25 mL of 0.1M HCl
B. 10 mL of 0.01M H2SO4 + 10 mL of 0.01M Ca(OH)2
C. 10 mL of 0.1M H2SO4 + 10 mL of 0.1M KOH
(a) for 10 mL of 0.2M Ca(OH)2 and 25 mL of 0.1M HCl
10 ml of 0.2 M Ca(OH)2= 10× 0.2 milimole = 2 milimoles
25 ml of 0.1 M HCl = 25× 0.1 milimole = 2.5 milimoles
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl ↔ CaCl2 + 2H2O
0.1 a mole of Ca(OH)2 reacts with 2 millimole of HCl
∴ 2.5 mole of HCl reacts with 1.25 millimole of Ca(OH)2
∴ Ca(OH)2 left = 1=1.25 = 0.75 milimole
Volume of reaction mixture = 10mL+ 25mL = 35mL
∴ Molarity of Ca(OH)2in the mixture solution is:
Molarity = 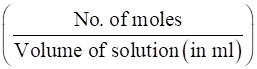
Hence,
Molarity = = 0.0214 M
= 0.0214 M
⇒[OH-] = 2 × 0.0124 M
⇒[OH-] = 0.0428 M
To caculate pOH, we use the formula:
pH = - log[OH-]
⇒pH= - log (4.28× 10-2)
⇒pH = -log 4.28 + 2log 10
⇒pH = 2 – 0.6314
⇒pH = 1.37
As we know that, pH + pOH =14
∴ pH = 14 – 1.37
⇒pH = 12.63
Hence, the pH is 12.62
(b) for 10 mL of 0.01M H2SO4 and 10 mL of 0.01M Ca(OH)2
10 ml of 0.01 M H2sO4 = 10× 0.01 milimole = 0.1 milimole
10 ml of 0.01 M Ca(OH)2 = 10× 0.01 milimole = 0.1 milimole
Ca(OH)2 + H2sO4 = CaSO4 + 2H2O
1 mole of Ca(OH)2 reacts with 1 mole of H2sO4
∴ 0.1 millimole of Ca(OH)2 will react completely with 0.1 minimal of H2SO4. Hence solution will be neutral with pH= 7
(C) 10 mL of 0.1M H2SO4 and 10 mL of 0.1M KOH
10 ml of 0.01 M H2sO4 = 10× 0.01 milimole = 0.1 milimole
10 ml of 0.1 M KOH = 10× 0.1 milimole = 1 milimole
2KOH+ H2sO4 = K2SO4 + 2H2O
I mole of KOHreacts with 0.5 milimole of H2sO4
∴ H2SO4 left = 1=0.5 = 0.5 milimole
Volume of reaction mixture = 10+ 10 = 20 mL
∴ Molarity of H2SO4 in the mixture solution is:
Molarity = 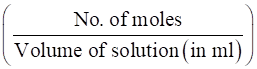
Hence,
Molarity = = 2.5 × 10-12 M
= 2.5 × 10-12 M
⇒[H+] = 2 × 2.5 × 10-12
⇒[H+] = 5× 10-2
To caculate pH, we use the formula:
pH = - log[H+]
⇒pH= - log (5× 10-2)
⇒pH = -log 5 + 2log 10
⇒pH = 2 – 0.699
⇒pH = 1.3
Hence, the pH is 1.3