Two equal circles touch each other externally at C and AB is a common tangent to the circles. Then, ∠ACB =
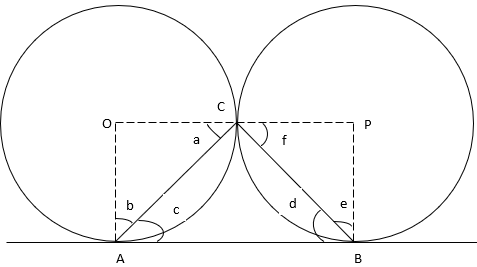
Property 1: The tangent at a point on a circle is at right angles to the radius obtained by joining center and the point of tangency.
Property 2: Sum of all angles of a straight line = 180°.
Property 3: Sum of all angles of a triangle = 180°.
By property 1, ∆OAB is right-angled at ∠OAB (i.e., ∠OAB = 90°) and ∆PBA is right-angled at ∠ PBA (i.e., ∠ PBA = 90°)
Clearly,
∠b + ∠c = ∠OAB
⇒ ∠b + ∠c = 90°
⇒ ∠b = 90° - ∠c
Similarly,
∠d + ∠e = ∠PBA
⇒ ∠d + ∠e = 90°
⇒ ∠e = 90° - ∠d
Now,
∠a = ∠b = 90° - ∠c [∵ OA = OC (Radius)]
And,
∠e = ∠f = 90° - ∠d [∵ PB = PC (Radius)]
By property 2,
∠a + ∠f + ∠ACB = 180°
⇒ ∠ACB = 180° – ∠a – ∠f
⇒ ∠ACB = 180° – (90° - ∠c) – (90° - ∠d)
⇒ ∠ACB = 180° – 90° + ∠c – 90° + ∠d
⇒ ∠ACB = ∠c + ∠d
Now, in ∆ACB
By property 3,
∠ACB + ∠c + ∠d = 180°
⇒ ∠ACB + ∠ACB = 180° [∵∠ACB = ∠c + ∠d]
⇒ 2∠ACB = 180°
![]()
⇒ ∠ACB = 90°
Hence, ∠ACB = 90°