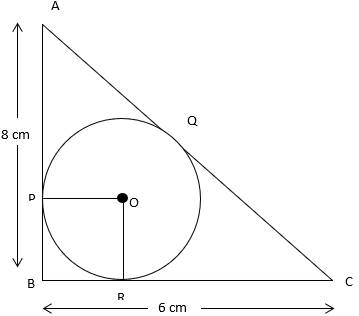
ABC is a right angled triangle, right angled at B such that BC = 6 cm and AB = 8 cm. A circle with centre O is inscribed in ΔABC. The radius of the circle is
Given:
BC = 6 cm
AB = 8 cm
Property 1: If two tangents are drawn to a circle from one external point, then their tangent segments (lines joining the external point and the points of tangency on circle) are equal.
Property 2: The tangent at a point on a circle is at right angles to the radius obtained by joining center and the point of tangency.
Property 3: Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral = 360°.
By property 1,
AP = AQ (Tangent from A)
BP = BR (Tangent from B)
CR = CQ (Tangent from C)
∵ ABC is a right-angled triangle, ∴ by Pythagoras Theorem
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ AC2 = 82 + 62
⇒ AC2 = 64 + 36
⇒ AC2 = 100
⇒ AC = √100
⇒ AC = 10 cm
Clearly,
AQ + QC = AC = 10 cm
⇒ AP + RC = 10 cm [∵ AQ = AP and QC = RC]
Also,
AB + BC = 8 cm + 6 cm = 14 cm
⇒ AP + PB + BR + RC = 14 cm [∵ AB = AP + PB and BC = BR + RC]
⇒ AP + RC + PB + BR = 14 cm
⇒ 10 cm + BR + BR = 14 cm [∵ AP + RC = 10 cm and PB = BR]
⇒ 10 cm + 2BR = 14 cm
⇒ 2BR = 14 cm – 10 cm = 4 cm
![]()
⇒ BR = 2 cm
Now,
∠BPO = 90° [By property 3]
∠BRO = 90° [By property 3]
∠PBM = 90° [Given]
Now by property 2,
∠BPO + ∠BRO + ∠PBM + ∠ROP = 360°
⇒ ∠ROP = 360° - ∠BPO + ∠BRO + ∠PBM
⇒ ∠ROP = 360° - (90° + 90° + 90°)
⇒ ∠ROP = 360° - 270°
⇒ ∠ROP = 90°
Now, ∵ ∠ROP = 90° and BP = BR which are adjacent sides
∴ Quadrilateral PBRO is a square
⇒ PO = BR = 2 cm
Hence, Radius = 2 cm