In Fig. 10.98, a circle touches the side DF of AEDF at H and touches ED and EF produced at K and M respectively. If EK = 9 cm, then the perimeter of ΔEDF is
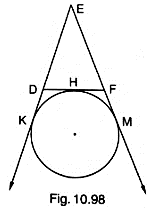
Given:
EK = 9 cm
Property: If two tangents are drawn to a circle from one external point, then their tangent segments (lines joining the external point and the points of tangency on circle) are equal.
By above property,
EM = EK = 9 cm (tangent from E)
DK = DH (tangent from D)
FM = FH (tangent from F)
Now,
Perimeter of ∆EDF = ED + DF + FE
⇒ Perimeter of ∆EDF = (EK – KD) + (DH + HF) + (EM – MF)
[∵ED = EK – KD
DF = DH + HF
FE = EM – MF]
⇒ Perimeter of ∆EDF = EK – KD + DH + HF + EM – MF
⇒ Perimeter of ∆EDF = EK – DH + DH + HF + EM – HF [∵DK = DH and FM = FH]
⇒ Perimeter of ∆EDF = EK + EM
⇒ Perimeter of ∆EDF = 9 cm + 9 cm
⇒ Perimeter of ∆EDF = 18 cm
Hence, Perimeter of ∆EDF = 18 cm