Locate ![]() and
and ![]() on the number line.
on the number line.
(i) √5
We can write 5 as the sum of the squares of two natural numbers: 5 = 1 + 4
⇒ 5 = 12 + 22
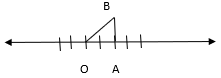
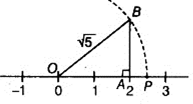
On the number line, take OA = 2 units.
Draw BA = 1 units, perpendicular to OA. Join OB.
By Pythagoras theorem, OB = √5 Using a compass with centre O and radius OB, draw an arc which intersects the number line at the point C. Then, C corresponds to √5.
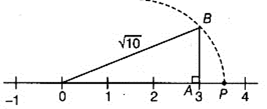
(ii) √10
We can write 10 as the sum of the squares of two natural numbers: 10 = 1 + 9
⇒ 10 = 12 + 32
On the number line, take OA = 3 units.
Draw BA = 1 units, perpendicular to OA. Join OB.
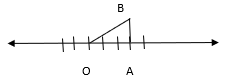
By Pythagoras theorem, OB = √10 Using a compass with centre O and radius OB, draw an arc which intersects the number line at the point C. Then, C corresponds to √10.
(ii). √17
We can write 17 as the sum of the squares of two natural numbers: 17 = 1 + 16
⇒ 17 = 12 + 42
On the number line, take OA = 4 units.
Draw BA = 1 units, perpendicular to OA. Join OB.
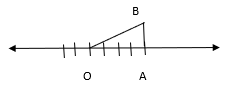
By Pythagoras theorem, OB = √17 Using a compass with centre O and radius OB, draw an arc which intersects the number line at the point C. Then, C corresponds to √17.
