Explain with diagrams what is meant by the “series combination” and “parallel combination” of resistances. In which case the resultant resistance is: (i) less, and (ii) more, than either of the individual resistances?
In a circuit, resistors are connected end-to-end are said to be in series, if the same current
exists in all of them through a single path. When resistances are connected in series, their equivalent resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
R = R1 + R2 + R3 + - - - - -
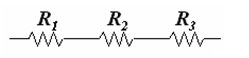
When resistances are connected in parallel, the reciprocal of their equivalent resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/ R3 + - - - - -
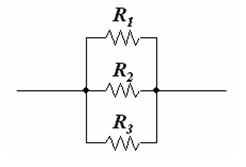
The resultant resistance is less than either of the individual resistances.