a. What is the least distance of distinct vision for a normal eye?
b. Does the above distance increase or decrease for a long- sighted eye? Give reason for your answer with diagram.
a. Human eye contains a natural convex lens & the retina is the screen. A normal person can see things clearly beyond 25 cm which is the least distance of distinct vision.
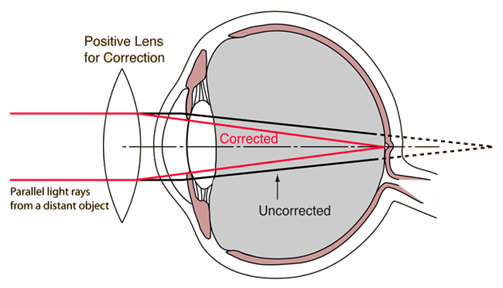
b. Long-sighted eye means the person is suffering from hypermetropia. The least distance of distinct vision increases in hypermetropia and the image is formed beyond the retina. In this defect, the light rays coming from the object placed between near point & the point of least distance of distinct vision, after refraction from the eye lens converges to a point beyond the retina. This implies that the image is formed beyond the eye thus creating a blurry image. In such cases, the focal length of the eye lens increases. So to bring the image on retina a double convex lens is used. The double convex lens converges the light rays coming from the object in front of the eye lens. In other words, the convex lens creates an image of the object at the near point. Now this image acts as an object for the eye lens and thus forming an image on the retina.