Explain the cleansing action of soap with the help of a diagram.
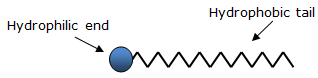
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chain carboxylic acids. They contain two ends having different properties: the carboxylic acid part which is hydrophobic and the ionic end (Na+ or K+) which is hydrophilic as shown in the following figure.
Dirt present in clothes is a hydrocarbon. When soap is used in water, the soap molecules tend to surround the dirt such that they form a cluster in which the hydrophobic tails are in the interior of the cluster and the hydrophilic part are on the surface of the cluster (see figure below). The hydrophilic part dissolves in water and the hydrophobic part dissolves in the hydrocarbon (dirt). This formation or cluster is called micelle.
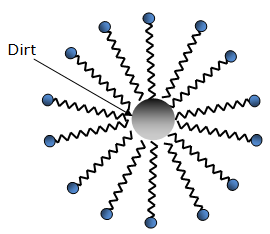
Agitating the water by hand or brush forces the hydrophilic end to move along the direction of flow of water, dragging the micelle out of the clothes and the dirt stuck to the micelle is rinsed away. In this way, soaps perform the cleansing action.