In a simple circuit of resistance R, self inductance L and voltage E, the current i at any time t is given by 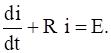 If E is constant and initially no current passes through the circuit, prove that
If E is constant and initially no current passes through the circuit, prove that 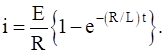
We know that in a circuit of R, L and E we have,
![]()
⇒ ![]()
We can see that it is a linear differential equation of the form ![]()
Where P = ![]() and Q =
and Q = ![]()
I.F = e∫Pdt
= e![]() dt
dt
= ![]()
Solution of the given equation is given by
i × I.F = ∫Q × I.F dt + c
⇒ i × ![]() = ∫
= ∫ ![]() ×
× ![]() dt + c
dt + c
⇒ i × ![]() = ∫
= ∫ ![]() ×
× ![]() dt + c
dt + c
⇒ i = ![]() + c
+ c ![]() ……(1)
……(1)
Initially, there was no current
So, at i = 0, t = 0
![]()
![]()
Now, putting the value of c in equation (1)
i = ![]() –
– ![]()
i = ![]() (1 –
(1 – ![]() )
)
10