Is 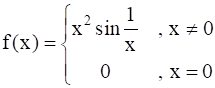 a continuous function?
a continuous function?
Basic Idea:
A real function f is said to be continuous at x = c, where c is any point in the domain of f if :
![]() where h is a very small ‘+ve’ no.
where h is a very small ‘+ve’ no.
i.e. left hand limit as x → c (LHL) = right hand limit as x → c (RHL) = value of function at x = c.
This is very precise, using our fundamental idea of the limit from class 11 we can summarise it as a function is continuous at x = c if :
![]()
Given :
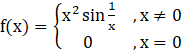 ……………….Equation 1
……………….Equation 1
As for x ≠ 0, f(x) is just a product of two everywhere continuous function
∴ it is continuous for all x ≠ 0.
∵ f(x) is changing its nature at x = 0, So we need to check continuity at x = 0
f(0) = 0 [using equation 1]
and ![]() = 0
= 0
[∵ sin(1/0) is also going to be a value between [–1,1] ,so its product with 0 = 0]
Thus,
![]()
∴ It is continuous at x = 0
Hence, it is everywhere continuous.