If y = x + tan x, show that: cos2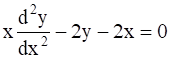
Basic idea:
√Second order derivative is nothing but derivative of derivative i.e. ![]()
√The idea of chain rule of differentiation: If f is any real-valued function which is the composition of two functions u and v, i.e. f = v(u(x)). For the sake of simplicity just assume t = u(x)
Then f = v(t). By chain rule, we can write the derivative of f w.r.t to x as:
![]()
√Product rule of differentiation- ![]()
√Apart from these remember the derivatives of some important functions like exponential, logarithmic, trigonometric etc..
Let’s solve now:
Given, y = x+ tan x …..equation 1
As we have to prove: cos2![]()
We notice a second-order derivative in the expression to be proved so first take the step to find the second order derivative.
Let’s find ![]()
As ![]()
So lets first find dy/dx and differentiate it again.
∴ ![]() [∵
[∵ ![]() tan x) = sec2 x &
tan x) = sec2 x & ![]() ]
]
![]()
∴ ![]()
Differentiating again with respect to x :
![]()
![]()
[ differentiated sec2x using chain rule, let t = sec x and z = t2 ∴ ![]() ]
]
![]() ……….equation 2
……….equation 2
As we got an expression for the second order, as we need cos2x term with ![]()
Multiply both sides of equation 1 with cos2x:
∴ we have,
![]() [∵ cos x × sec x = 1]
[∵ cos x × sec x = 1]
![]()
From equation 1:
tan x = y – x![]()
![]() ….proved
….proved