Verify Lagrange’s mean value theorem for the following functions on the indicated intervals. In each find a point ‘c’ in the indicated interval as stated by the Lagrange’s mean value theorem :
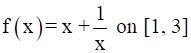
Lagrange’s mean value theorem states that if a function f(x) is continuous on a closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b), then there is at least one point x=c on this interval, such that
f(b)−f(a)=f′(c)(b−a)
![]()
This theorem is also known as First Mean Value Theorem.
![]()
![]()
∴ f(x) is continuous in [1, 3]
![]()
Differentiating with respect to x:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Here,
![]()
⇒ f’(x) exists for all values except 0
∴ f(x) is differentiable in (1, 3)
So both the necessary conditions of Lagrange’s mean value theorem is satisfied.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
On differentiating with respect to x:
![]()
For f’(c), put the value of x=c in f’(x):
![]()
For f(3), put the value of x=3 in f(x):
![]()
![]()
![]()
For f(1), put the value of x=1 in f(x):
![]()
⇒ f(1) = 2
![]()
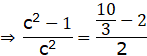
![]()
![]()
![]()
⇒ 6(c2 – 1) = 4c2
⇒ 6c2 – 6 = 4c2
⇒ 6c2 – 4c2 = 6
⇒ 2c2 = 6
![]()
⇒ c2 = 3
![]()
Hence, Lagrange’s mean value theorem is verified.