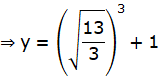Find a point on the curve y = x3 + 1 where the tangent is parallel to the chord joining (1, 2) and (3, 28).
Lagrange’s mean value theorem states that if a function f(x) is continuous on a closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b), then there is at least one point x=c on this interval, such that
f(b)−f(a)=f′(c)(b−a)
![]()
This theorem is also known as First Mean Value Theorem.
Let f(x) = x3 + 1 on [1, 3]
This interval [a, b] is obtained by x – coordinates of the points of the chord.
Every polynomial function is continuous everywhere on (−∞, ∞) and differentiable for all arguments.
Here, f(x) is a polynomial function. So it is continuous in [1, 3] and differentiable in (1, 3). So both the necessary conditions of Lagrange’s mean value theorem is satisfied.
![]()
![]()
![]()
f(x) = x3 + 1
Differentiating with respect to x:
f’(x) = 3x2
For f’(c), put the value of x=c in f’(x):
f’(c)= 3c2
For f(3), put the value of x=3 in f(x):
f(3)= (3)3 + 3
= 27 + 3
= 30
For f(1), put the value of x=1 in f(x):
f(1) = (1)3 + 3
= 1 + 3
= 4
![]()
![]()
![]()
⇒ 3c2 = 13
![]()
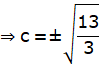
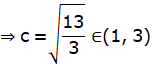
We know that, the value of c obtained in Lagrange’s Mean value Theorem is nothing but the value of x – coordinate of the point of the contact of the tangent to the curve which is parallel to the chord joining the points (1, 2) and (3, 28).
Now, Put this value of x in f(x) to obtain y:
y = x3 + 1