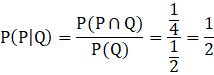A couple has two children. Find the probability that both the children are
(i) males, if it is known that at least one of the children is male.
(ii) females, if it is known that the elder child is a female.
Let b and g represents the boy and the girl child respectively.
Now if a family has two children, the sample space will be
S = {(b, b), (b, g), (g, b), (g, g)}, n(S)=4
(i) Let A be the event that both children are males, then
A= {(b, b)}, n(A)=1
So the probability that both children are males is
![]()
Let B be the event that at least one of the children is male
Then B = {(b, b), (b, g), (g, b)}, n(B) = 3
And the corresponding probability becomes
![]()
The sample space for the at least male and both being male will become
(A∩B) = {(b, b)}, n(A∩B)=1
And the corresponding probability becomes
![]()
So the conditional probability that both are males given that the at least one is male is
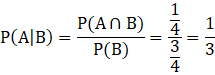
(ii) Let P be the event that both children are females, then
P= {(g, g)}, n(P)=1
So the probability that both children are females is
![]()
Let Q be the event that the elder child is a female
Then Q = {(g, b), (g, g)}, n(Q) = 2
And the corresponding probability becomes
![]()
The sample space for the elder child being female and both child being female will become
(P∩Q) = {(g, g)}, n(P∩Q)=1
And the corresponding probability becomes
![]()
So the conditional probability that if the elder child is female then both children are females is