Using differentials, find the approximate values of the following:
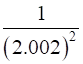
Let us assume that ![]()
Also, let x = 2 so that x + Δx = 2.002
⇒ 2 + Δx = 2.002
∴ Δx = 0.002
On differentiating f(x) with respect to x, we get
![]()
![]()
We know![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
When x = 2, we have![]()
![]()
![]()
Recall that if y = f(x) and Δx is a small increment in x, then the corresponding increment in y, Δy = f(x + Δx) – f(x), is approximately given as
![]()
Here, ![]() and Δx = 0.002
and Δx = 0.002
⇒ Δf = (–0.25)(0.002)
∴ Δf = –0.0005
Now, we have f(2.002) = f(2) + Δf
![]()
![]()
⇒ f(2.002) = 0.25 – 0.0005
∴ f(2.002) = 0.2495
Thus, ![]()
9