Evaluate the integral:
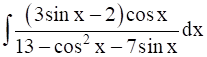
I =![]() =
= ![]()
⇒ I = ![]()
Let, sin x = t ⇒ cos x dx = dt
∴ I = ![]()
As we can see that there is a term of t in numerator and derivative of t2 is also 2t. So there is a chance that we can make substitution for t2 – 7t + 12 and I can be reduced to a fundamental integration.
As, ![]()
∴ Let, 3t – 2 = A(2t – 7) + B
⇒ 3t – 2 = 2At – 7A + B
On comparing both sides –
We have,
2A = 3 ⇒ A = 3/2
–7A + B = –2 ⇒ B = 7A – 2 = 17/2
Hence,
I = ![]()
∴ I = ![]()
Let, I1 =![]() and I2 =
and I2 = ![]()
Now, I = I1 + I2 ….eqn 1
We will solve I1 and I2 individually.
As, I1 = ![]()
Let u = t2 – 7t + 12 ⇒ du = (2t – 7)dx
∴ I1 reduces to ![]()
Hence,
I1 = ![]() {∵
{∵ ![]() }
}
On substituting value of u, we have:
I1 = ![]() ….eqn 2
….eqn 2
As, I2 = ![]() and we don’t have any derivative of function present in denominator. ∴ we will use some special integrals to solve the problem.
and we don’t have any derivative of function present in denominator. ∴ we will use some special integrals to solve the problem.
As denominator doesn’t have any square root term. So one of the following two integrals will solve the problem.
![]()
∵ I2 = ![]()
⇒ I2 = ![]()
Using: a2 – 2ab + b2 = (a – b)2
We have:
I2 =![]()
I2 matches with the form ![]()
∴ I2 =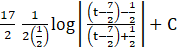
I2 =![]()
![]() …eqn 3
…eqn 3
From eqn 1, we have:
I = I1 + I2
Using eqn 2 and 3, we get –
I = ![]()
Putting value of t in I:
I = ![]() …..ans
…..ans